
IRMA Autonomous Mobile Robot Research
Coordinator (PI): Tomás Arredondo
Contributors: Tomás Arredondo, Wolfgang Freund, César Muñoz, Nicolás Navarro, Fernando Quirós
Start Date: 1st July 2005
End Date: 1st December 2009
This project study and develop behavior based mobile robots. Initially, the project focused on developing new algorithm and methods for mobile robot applications with reduced sensory capabilities or with low cost sensors and actuators. The principal methods that we use include genetic algorithms, genetic programming and fuzzy logic.
Since 2007, the project study state of art algorithms and architectures to determine capabilities and limitations in real world setups. In order to make this process more efficient we divide the process into two stages. In the first stage, we utilize mobile robot simulators. In the second stage, we adapt and develop new algorithms capable of completing tasks in real world scenarios.
The project was started by Prof. Tomás Arredondo, Nicolás Navarro, César Muñoz on the second half of 2005 after a seminar on artificial intelligence.
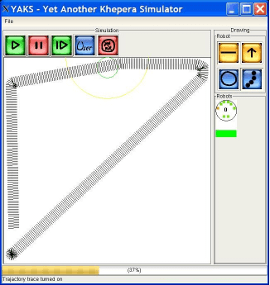
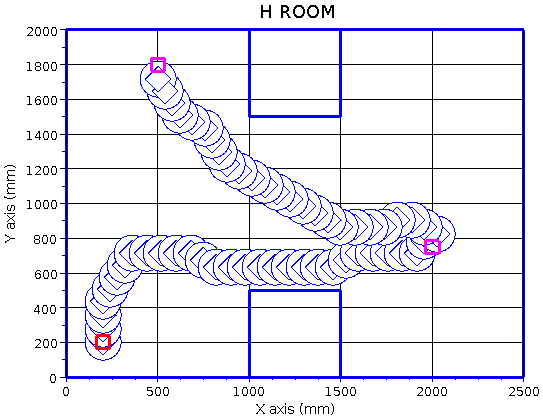
Example of different trajectories generated by our genetic algorithms and fuzzy motivations approach. Left, trajectories displayed in YAKS. Right, trayectories displayed using scilab.
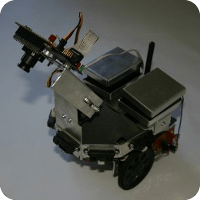
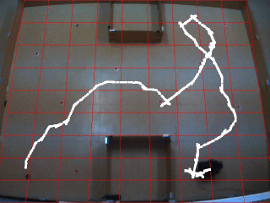
Left, IRMA-II, our mobile robot platform. Right, Real-world results recorded by a ceilling camera
Project Partners:
Related Publications:
-
Fuzzy Motivations in a Multiple Agent Behaviour-Based Architecture
International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems. vol. 10, no. 313, pp. 1-13. Aug 2013. Arredondo, Tomás; Freund, Wolfgang; Navarro-Guerrero, Nicolás; Castillo, Patricio
DOI, PDF, URL, bib file. bibkey: Arredondo2013Fuzzy ©2013 CC BY 3.0 Copyright Arredondo et al. -
Desarrollo e implementación de algoritmo evolutivo multi-objectivo para generar rutas online en un robot móvil autónomo
Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María. Valparaíso, Chile. Dec 2009. Language: Spanish Navarro-Guerrero, Nicolás
URL, bib file. bibkey: Navarro-Guerrero2010Desarrollo ©2009 Copyright Navarro-Guerrero -
Cooperative Adaptive Behavior Acquisition in Mobile Robot Swarms Using Neural Networks and Genetic Algorithms
Electronics, Robotics and Automotive Mechanics Conference (CERMA). pp. 417-421. Morelos, Mexico. Sep 2008. Muñoz, César; Navarro, Nicolás; Arredondo, Tomás; Freund, Wolfgang
DOI, URL, bib file. bibkey: Munoz2008Cooperative ©2008 IEEE -
Real-Time Adaptive Fuzzy Motivations for Evolutionary Behavior Learning by a Mobile Robot
Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (MICAI) - Advances in Artificial Intelligence. vol. 4293 of LNCS, pp. 101-111. Apizaco, Mexico. Nov 2006. Freund, Wolfgang; Arredondo Vidal, Tomás; Muñoz, César; Navarro, Nicolás; Quirós, Fernando
DOI, PDF, URL, bib file. bibkey: Freund2006Real ©2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg -
Acquiring Adaptive Behaviors of Mobile Robots Using Genetic Algorithms and Artificial Neural Networks
Electronics, Robotics and Automotive Mechanics Conference (CERMA). vol. 1, pp. 87-91. Cuernavaca, Mexico. Sep 2006. Navarro, Nicolás; Muñoz, César; Freund, Wolfgang; Arredondo, Tomás
DOI, PDF, URL, bib file. bibkey: Navarro2006Acquiring ©2006 IEEE -
Fuzzy Motivations for Evolutionary Behavior Learning by a Mobile Robot
International Conference on Industrial, Engineering and Other Applications of Applied Intelligent Systems (IEA/AIE). vol. 4031 of LNCS, pp. 462-471. Annecy, France. Jun 2006. Arredondo, Tomás; Freund, Wolfgang; Muñoz, César; Navarro, Nicolás; Quirós, Fernando
DOI, PDF, URL, bib file. bibkey: Arredondo2006Fuzzy ©2006 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg -
A Neural Approach for Robot Navigation Based on Cognitive Map Learning
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). pp. 1146-1153. Brisbane, QLD, Australia. Jun 2006. Yan, Wenjie; Weber, Cornelius; Wermter, Stefan
DOI, URL, bibkey: Yan2012Neural ©2006 IEEE